Chargebacks have become a significant issue for businesses, especially in e-commerce, costing over $20 billion annually in lost revenue. Chargebacks occur when cardholders dispute a charge, leading to refunds and additional fees for merchants. Understanding the causes of chargebacks is crucial for businesses to mitigate losses. Let’s examine the primary causes and practical ways to prevent them.
Types of Chargebacks
Chargebacks can be categorized into three main types:
- Merchant Error
- Criminal Fraud
- Friendly Fraud
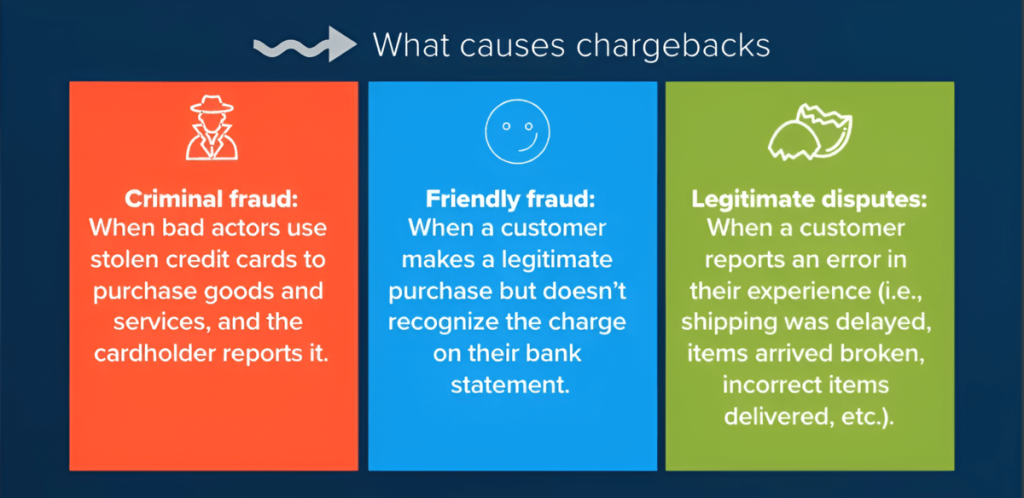
1. Merchant Error
Merchant errors account for 20-40% of chargebacks. These errors include billing mistakes, misleading product descriptions, and fulfillment issues. Common errors are:
- Incorrect product descriptions or misleading advertising: If the delivered product does not match its description, customers may file a dispute.
- Billing discrepancies: Charging the wrong amount or using an unclear business name can confuse customers.
- Fulfillment problems: These include late shipments, damaged goods, or incomplete orders, accounting for 15-20% of chargebacks.
2. Criminal Fraud
Criminal fraud involves the use of stolen card information for unauthorized purchases. 58% of chargebacks related to fraud occur in online transactions (card-not-present). EMV chips have reduced in-person fraud, but online fraud remains a serious issue. To prevent criminal fraud:
- Use fraud detection tools like 3D Secure, address verification systems (AVS), and tokenization.
- Monitor unusual activity, such as large orders from new customers.
3. Friendly Fraud
Friendly fraud occurs when legitimate transactions are disputed. Mastercard reports that 40-50% of chargebacks fall under this category. Common examples include:
- Buyer’s remorse: Customers change their minds after purchasing but do not request a refund.
- Unrecognized purchases: Family members may make purchases, and the cardholder may not recognize the transaction.
- Subscription-related issues: Forgotten or misunderstood recurring payments often lead to chargebacks.
| Chargeback Types | Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Merchant Error | Incorrect billing, product misrepresentation, late shipping | Clear descriptions, consistent billing names, responsive customer service |
| Criminal Fraud | Stolen card information | Use fraud detection tools like 3D Secure, monitor transactions |
| Friendly Fraud | Buyer’s remorse, forgotten purchases, subscription disputes | Refund policies, subscription reminders, blacklist repeat offenders |
Common Causes of Chargebacks
Chargebacks can arise from several factors beyond the broad categories mentioned above. The most frequent causes include:
1. Product or Service Quality Issues
Product quality issues account for 34% of chargebacks. Examples include:
- Damaged or faulty products: Customers may file disputes if products do not function as advertised.
- Unmet expectations: Variations in product appearance or function from the description (e.g., wrong size or color) can trigger chargebacks.
- Counterfeit goods: Receiving counterfeit items is a major reason for disputes, particularly in industries like fashion and electronics.
2. Shipping Issues
Shipping problems such as late deliveries, lost packages, or damaged goods are responsible for 22% of chargebacks. Customers often dispute charges when packages are late or damaged, even though merchants may not have direct control over shipping processes. To prevent these disputes:
- Provide accurate shipping estimates.
- Offer tracking numbers and maintain clear communication about potential delays.
3. Billing Errors
Billing mistakes contribute to 15% of chargebacks. Customers may file disputes if they are charged the wrong amount or if the business name on their statement does not match the one they recognize.
| Chargeback Causes | Percentage of Total Chargebacks | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Product/Service Issues | 34% | Ensure product quality, accurate descriptions |
| Shipping Issues | 22% | Provide tracking info, accurate shipping estimates |
| Billing Errors | 15% | Use consistent billing names, prevent overcharges |
| Criminal Fraud | 20% | Implement fraud detection, monitor transactions |
| Friendly Fraud | 40-50% | Offer clear refund options, implement subscription reminders |

Preventing Chargebacks
Preventing chargebacks requires a proactive approach across multiple areas of business operations. Below are strategies that can significantly reduce chargeback occurrences:
1. Customer Service Management
Responsive customer service plays a key role in preventing chargebacks. 68% of chargebacks can be resolved by addressing issues before they escalate. Merchants should:
- Respond to customer complaints promptly.
- Offer refunds or replacements without delays.
- Provide clear, easy-to-find return and refund policies.
2. Fraud Detection Tools
Using fraud detection systems is crucial to avoid fraudulent transactions. Fraud prevention tools like 3D Secure 2.0, AVS, and tokenization help reduce fraud-related chargebacks. Dynamic fraud detection models are recommended by payment processors like Checkout.com and Stripe for their adaptability to changing patterns.
3. Subscription Billing Management
Subscription services are particularly vulnerable to chargebacks. Merchants should provide reminders before renewing subscriptions and offer a straightforward cancellation process. Merchanto.org, an official partner of VISA and Mastercard, provides tools for managing recurring payments and minimizing disputes. Businesses can explore Merchanto.org to manage their subscription billing more efficiently.
4. Accurate Record-Keeping
Merchants should maintain detailed records of all transactions, including communication with customers and proof of delivery. This documentation helps in disputing chargebacks. Stripe and Braintree advise keeping transaction records to strengthen your case during chargeback disputes.
5. Clear and Consistent Communication
Preventing disputes also requires clear and consistent communication with customers. Clear terms of service, including return policies and shipping details, reduce misunderstandings that could lead to chargebacks. Businesses should:
- Use simple, clear language on their websites.
- Send reminders for recurring charges and offer simple cancellation options.
- Ensure consistent communication regarding order status, shipping details, and delays.
| Prevention Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Responsive customer service | Resolves up to 68% of disputes before escalation |
| Fraud detection tools | Reduces 85% of fraud-related chargebacks |
| Accurate record-keeping | Helps win 70-80% of chargeback representments |
| Clear communication and policies | Prevents chargebacks related to misunderstandings |
The Chargeback Process
Chargebacks follow a strict process that typically spans 60–90 days. Merchants must understand this process to better manage disputes. Here’s a breakdown:
- Transaction occurs: The cardholder makes a purchase.
- Dispute initiation: The cardholder disputes the charge, triggering the chargeback process.
- Evidence submission: The merchant must provide evidence such as invoices, receipts, or proof of delivery.
- Bank review: The issuing bank reviews the evidence provided and makes a decision on whether to reverse the transaction or uphold it.
- Arbitration: If the merchant disagrees with the bank’s decision, the case can move to arbitration, where the final decision is made.
Understanding the chargeback process is essential for managing disputes and minimizing revenue loss.
Conclusion
Chargebacks can impose significant costs on businesses, but understanding their causes helps reduce their occurrence. By addressing merchant errors, using fraud detection tools, and mitigating friendly fraud, businesses can lower their chargeback rates. Responsive customer service, clear subscription management, and accurate record-keeping are critical in preventing disputes.
| Chargeback Prevention Summary | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Proactive customer service | Resolves disputes before they escalate |
| Fraud detection systems | Reduces fraudulent chargebacks significantly |
| Accurate record-keeping | Strengthens dispute defense, reducing financial losses |
| Clear billing practices | Minimizes customer confusion and subscription disputes |
By implementing these strategies, businesses can safeguard their revenue and reduce the impact of chargebacks on their operations.



