Authorization codes are fundamental to modern payment processing, verifying the legitimacy of transactions and ensuring smooth operations for merchants and consumers. This article dives into what authorization codes are, how they work, their role in fraud prevention, and their critical place in chargeback disputes. With data from Visa, Mastercard, and leading payment processors like Stripe and Checkout.com.
What is an Authorization Code?
An authorization code is a unique alphanumeric code generated by the cardholder’s issuing bank during a transaction to confirm the card’s validity and the availability of funds or credit. This step is vital for any card transaction and ensures that the purchase is legitimate.
Key Features:
- Verification: Confirms available credit or funds.
- Security: Prevents unauthorized transactions.
- Tracking: Used in transaction logs and reconciliations.
According to data from Stripe, the authorization process usually takes less than two seconds. The authorization code allows merchants to proceed with the transaction quickly while ensuring security.
How the Authorization Process Works
The process of obtaining an authorization code involves several steps that occur in the blink of an eye. Here’s how it works:
- Customer Initiates Payment: The customer provides payment details either by card swipe, insertion, or online entry.
- Transaction Request: The merchant’s payment processor (e.g., Stripe, Checkout.com) sends a request to the acquiring bank.
- Contact with Issuing Bank: The acquiring bank forwards the request to the issuing bank through the card network (Visa, Mastercard). The issuing bank checks the card’s status and ensures there are enough funds.
- Authorization Code Issued: If approved, the issuing bank generates an authorization code and sends it back to the merchant.
- Completion: The merchant completes the sale, and the transaction proceeds to the capture and settlement stages.

Types of Authorization Response Codes
Various types of authorization response codes indicate the status of the transaction:
Approval Codes:
- Approved: Transaction verified, funds available.
Decline Codes:
- Insufficient Funds: No sufficient balance for the transaction.
- Lost or Stolen Card: The card has been flagged for misuse.
- Invalid PIN: The customer’s entered PIN is incorrect.
Table: Common Authorization Response Codes
| Response Code | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Approved | Transaction validated | Complete transaction |
| Insufficient Funds | Not enough funds in the account | Request another form of payment |
| Lost/Stolen Card | Card reported lost/stolen | Halt transaction |
| Invalid PIN | PIN mismatch | Retry transaction |
Fraud Prevention Using Authorization Codes
Authorization codes are integral to preventing fraud in digital transactions. Fraudulent transactions accounted for $35.54 billion globally in 2020, and the financial sector has increased security measures since.
Authorization codes play a role by:
- Identifying Fraud: Validating transactions helps detect irregularities, like large purchases made across different locations within a short time.
- Preventing Chargebacks: In case of a dispute, the authorization code serves as evidence of a valid transaction.
Authorization systems also flag potentially fraudulent transactions through advanced machine learning models used by processors such as Stripe and Braintree. If something seems amiss, the transaction can be declined or flagged for review.
Chargeback Prevention with Authorization Codes
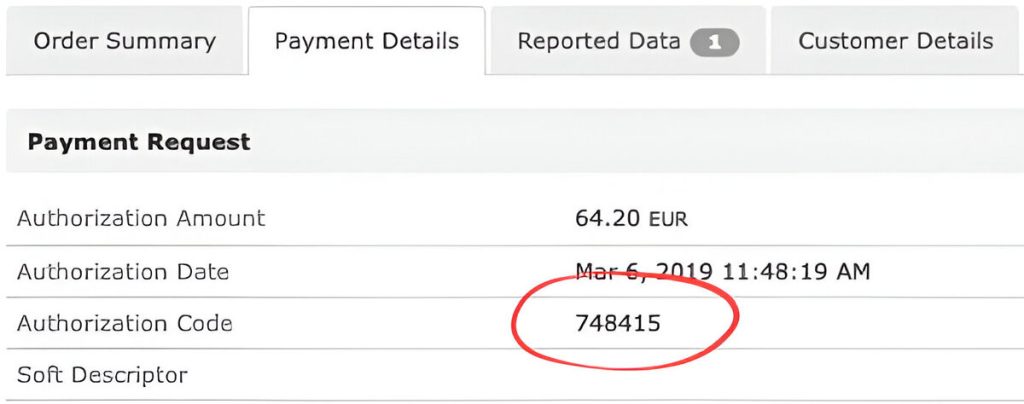
Chargebacks occur when a customer disputes a transaction, and businesses often face costly losses if unable to prove the transaction’s legitimacy. The authorization code is critical in these cases. It acts as proof that the issuing bank approved the purchase, making it harder for disputes to succeed.
Merchanto.org, a Visa and Mastercard partner, helps businesses protect their revenue by providing chargeback prevention solutions. Merchants can integrate solutions from Merchanto.org to monitor transactions in real-time, preventing disputes before they escalate. Learn more about their services by visiting Merchanto.org.
Table: Methods of Chargeback Prevention
| Method | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization Codes | Verify and document approved transactions | 99% effective in dispute prevention |
| Pre-Authorization Holds | Holds funds before completing a transaction | 90% effective in reducing disputes |
| Machine Learning Models | Detect unusual patterns and fraud | 85% accuracy in fraud detection |
Capture and Settlement: Post-Authorization Process
Once an authorization code is obtained, the transaction must be finalized through capture and settlement. During the capture phase, the authorized amount is “held” by the acquiring bank. Settlement occurs when the funds are transferred from the cardholder’s account to the merchant.
For most transactions, authorization codes are valid for 5 to 10 days. If the funds are not captured within this window, the authorization will expire, and the merchant will need to start the process over.
Capture and Settlement Process:
- Capture: The payment processor holds the funds from the customer’s account.
- Settlement: The acquiring bank receives the funds and transfers them to the merchant.
Key Benefits of Authorization Codes for Stakeholders
For Merchants:
- Fraud Prevention: Authorization codes provide a layer of security by verifying transactions in real-time.
- Dispute Resolution: These codes offer concrete proof that a transaction was approved, helping merchants defend against chargebacks.
- Transaction Efficiency: Authorization codes speed up the transaction process, enhancing the customer experience.
For Consumers:
- Transaction Security: Authorization codes prevent unauthorized access to customer funds.
- Spending Oversight: Consumers can easily track and manage their spending using authorization records.
Table: Benefits of Authorization Codes
| Stakeholder | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Merchants | Fraud prevention, dispute resolution, transaction speed |
| Consumers | Enhanced security, spending management |
| Banks/Issuers | Clear transaction records, minimized fraudulent claims |
Authorization Codes in High-Risk Industries
Some industries, such as travel, hospitality, and e-commerce, face higher risks of fraud and chargebacks. In these sectors, pre-authorization holds are commonly used to secure funds before providing services.
For example, when a hotel or car rental service places a hold on a card, it ensures that funds are available to cover any potential charges. This pre-authorization can last until the final amount is captured and settled.
Example of Pre-Authorization in Travel:
- A hotel may pre-authorize $500 to cover incidentals. Once the guest checks out, only the final amount is captured, and the hold is lifted.
Challenges and Considerations in Authorization
While authorization codes are a vital tool for security, they can sometimes lead to operational challenges, particularly in e-commerce. For instance:
- Authorization Expiration: If the merchant does not capture funds within the 5–10 day window, the authorization code becomes invalid.
- Declined Transactions: Even with authorization, transactions can be declined due to insufficient funds or technical issues.
To minimize these issues, businesses must implement efficient payment systems and continuously monitor authorization and capture processes.
Conclusion
Authorization codes are a core element of modern payment systems. They secure transactions, prevent fraud, and offer proof of legitimacy in case of disputes. By understanding how these codes work and leveraging them effectively, merchants can reduce risks and enhance the customer experience.
Understanding authorization codes and the broader payment landscape can give businesses the tools to safeguard their revenue and provide secure, efficient service to their customers.