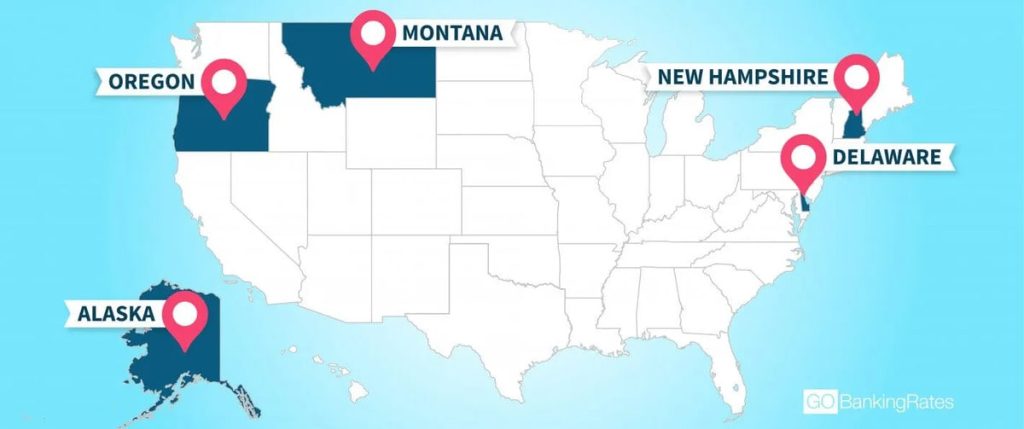
Sales tax is a common form of taxation in the U.S., but not all states impose it. Five states—Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon—do not collect statewide sales tax. This article covers how these states operate without sales tax and the other taxes they rely on for revenue.
States Without Sales Tax
In the U.S., 45 states and Washington, D.C. collect a statewide sales tax. However, five states operate without it. Here’s how these states generate revenue and the implications for residents and businesses.
1. Alaska
Alaska does not have a statewide sales tax, but local governments can impose taxes. Alaska’s revenue primarily comes from oil, allowing the state to have lower taxes overall.
- Local Sales Tax: Up to 7.5%.
- Average Local Sales Tax: 1.76%.
- Income Tax: None.
- Property Tax: Median rate of $3,464.
Key Facts:
- Anchorage and Fairbanks have no local sales tax, while Juneau has a 5% rate.
- Residents receive an annual dividend from oil revenues, the Permanent Fund Dividend, which can be a significant benefit.
| City | Sales Tax Rate | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Anchorage | 0% | 291,538 |
| Fairbanks | 0% | 32,515 |
| Juneau | 5% | 31,974 |
| Sitka | 5% | 8,689 |
| Ketchikan | 6.5% | 8,289 |
2. Delaware
Delaware has no state or local sales tax. Instead, it imposes a gross receipts tax on businesses, which is a percentage of total sales.
- Gross Receipts Tax: Ranges from 0.0945% to 0.7468%, depending on the business.
- Income Tax: Progressive, from 2.2% to 6.6%.
- Property Tax: One of the lowest in the U.S., with a median of $1,570.
| Business Type | Gross Receipts Tax |
|---|---|
| Retail | 0.7468% |
| Wholesale | 0.3947% |
| Food & Beverage | 0.6375% |
3. Montana
Montana has no statewide sales tax. Some tourist-heavy areas impose local taxes on specific items like lodging or car rentals.
- Income Tax: Progressive, from 1% to 6.75%, with a reduction to 5.9% in 2024.
- Property Tax: Median is $2,189.
Key Facts:
- Tourist towns like West Yellowstone and Big Sky impose a 3% resort tax on goods and services.
4. New Hampshire
New Hampshire doesn’t have general sales tax, but it levies taxes on prepared meals, lodging, and car rentals. Additionally, there is a timber tax of 10% on the value of harvested wood.
- Meals and Rentals Tax: 8.5%.
- Property Tax: High, with a median rate of $6,036.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Meals & Rentals Tax | 8.5% |
| Timber Tax | 10% |
| Property Tax (Median) | $6,036 |
5. Oregon
Oregon does not have a statewide sales tax. Some municipalities impose small taxes, but they are limited.
- Income Tax: Progressive, from 4.75% to 9.9%.
- Property Tax: Median rate of $3,352.
Key Facts:
- The city of Ashland has a 5% tax on prepared food.
How These States Generate Revenue Without Sales Tax
These five states, while not collecting sales tax, still require funding for public services. They rely more heavily on other forms of taxation, such as income tax, property tax, and excise taxes.
Table: Comparison of Revenue Sources in States Without Sales Tax
| State | Income Tax Rate | Property Tax (Median) | Sales Tax | Special Taxes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska | None | $3,464 | Local up to 7.5% | Oil excise taxes, tourism-related taxes |
| Delaware | 2.2%-6.6% | $1,570 | None | Gross receipts tax on businesses |
| Montana | 1%-6.75% (5.9% in 2024) | $2,189 | None | Resort tax up to 3% in tourist towns |
| New Hampshire | None on general income | $6,036 | None | Meals & rentals tax, timber tax |
| Oregon | 4.75%-9.9% | $3,352 | None | 5% tax on prepared food in some cities |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Living in States Without Sales Tax
States without sales tax offer several advantages for consumers, but they also come with trade-offs, primarily in other areas of taxation.
Benefits:
- Lower Purchase Costs: Consumers save money on goods and services.
- Cross-Border Shopping: Many people from neighboring states shop in tax-free states to save on large purchases.
Drawbacks:
- Higher Property Taxes: In states like New Hampshire, property taxes are significantly higher than the national average.
- Higher Income Taxes: Oregon and Delaware have higher income taxes than most states.
Sales Tax and E-Commerce
E-commerce has shifted the sales tax landscape. After the 2018 South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc. decision, states can require online businesses to collect sales tax even without a physical presence. This change affects businesses operating in tax-free states, especially those selling to customers in states with sales taxes.
Businesses navigating these complexities must ensure compliance with evolving sales tax laws. Merchanto.org, a trusted partner of VISA and MasterCard in chargeback prevention, helps businesses handle transaction disputes and remain compliant. More information is available at Merchanto.org.
The Role of Other Taxes in Tax-Free States
Without sales tax, these states rely on other taxes to cover government expenses. The absence of sales tax can make consumer purchases cheaper, but income and property taxes are often higher to compensate.
| State | Income Tax | Property Tax | Excise Taxes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska | None | Higher than average | Oil taxes, excise taxes on tourism goods |
| Delaware | 2.2%-6.6% | Low | Gross receipts tax |
| Montana | 1%-6.75% (5.9% in 2024) | Lower than average | Resort taxes in tourist towns |
| New Hampshire | None | High | Meals, rentals, timber taxes |
| Oregon | 4.75%-9.9% | Average | Local food taxes in some municipalities |
Effects of No Sales Tax on Business
Businesses in these states may face unique challenges. For instance, the absence of sales tax can attract shoppers from neighboring states, boosting local business. However, the lack of sales tax may mean higher operational costs due to increased income or gross receipts taxes.
For businesses, compliance with sales tax laws is critical, particularly when selling online across state borders.
Conclusion
Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon are unique in not collecting statewide sales tax. While this can lead to savings on consumer purchases, these states rely on other taxes like income, property, and excise taxes to generate revenue. For businesses operating in these regions, navigating tax compliance—especially with e-commerce—is crucial.



